SAP as an ERP facilitates its customers to cover all business processes - simple processes and complex processes. Organizational Business transactions are available in SAP standard functionality, which can be customized and configured as per our industry and Company specifics. Higher the level of integration, easier is the mapping of these economical business situations. SAP has Various Modules and they are integrated with each other as a system. Various SAP Functional Modules provided by SAP are:
SAP FINANCE
SAP CONTROLLING
SAP TREASURY
SAP MATERIALS MANAGEMENT
SAP PRODUCTION PLANNING
SAP SALES DISTRIBUTION
SAP QUALITY MANAGEMENT
SAP PROJECT SYSTEM
SAP HUMAN RESOURCE
SAP PLANT MAINTAINENCE
SAP LOGISTICS AND MAINTENANCE
Now all of these modules are integrated at different levels with FI considering its impact on the books of accounts. Some transactions do not affect any financial transaction and therefore there is no change in the FI system. FI also has various sub modules as specified below. Each needs to be studied in detail to know the effect of the same in the system. The sub modules also integrate with the above Modules to provide cross modular FI entries. For example SAP FI-AP (Accounts Payable) is connected to SAP Materials Management. The scenario here is obvious as it involves the Purchase to Pay Cycle.
The Various SAP FINANCIAL SUB MODULES are:
SAP FI-GL – GENERAL LEDGER
SAP FI- AR – ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLES
SAP FI- AP – ACCOUNTS PAYABLES
SAP FI-AA – ASSET ACCOUNTING
SAP FI- BL – BANK ACCOUNTING
SAP FI – SL – SPECIAL PURPOSE LEDGER
The understanding of each sub module is an in-depth subject. For now let us understand the FI-MM integration. To understand the SAP Process and its steps it would be necessary for the once to understand a practical business scenario.
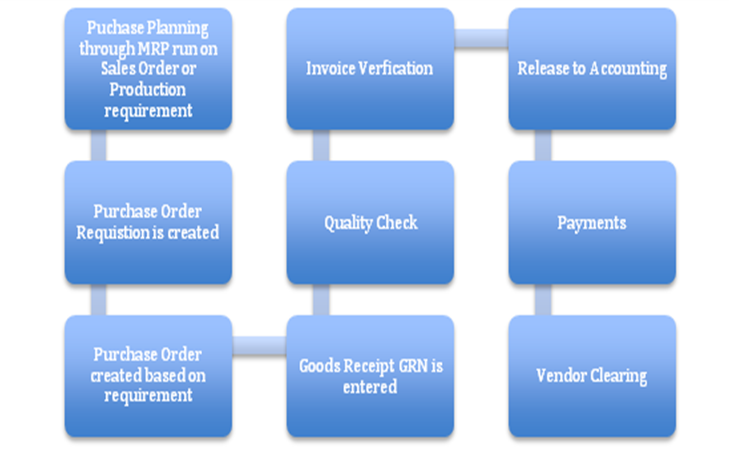
How a Purchase to Pay Cycle works
Also called Procurement to Payment, it involves all the steps in a real time scenario involving the initiation of Goods requirement to its receipt invoicing and Payment are available in standard SAP. The detailed steps in the business scenario would be:
- Production Planning (Requirements of Raw Material) or Purchase Planning.
- Create Production Order or Purchase Order.
- Quotations
- Goods received
- Quality Check
- Updating Stock
- Billing
- Approval of Payment
Now to Map this scenario in SAP the following Standard Procedure could be used:
In SAP Modules Data is stored in tables. There are master data created at Functional end for every module. What are Master Data? Information entered in the system which can be used repeatedly without entering the same data again and again is called a Master data. For example Vendor, Customers, GL all are master data in SAP system. These master data can be called from various data entry screens in SAP. Therefore, for a Vendor or a customer, details like address, Pincode, Email, and contact Number need not be entered more than once.
Now what are the FINANCIAL entries that incur in the above process and where do the books of accounts get updated?
- PurchasePlanning – No FI entry it is just an order no Financial impact in the transaction.
- Purchase Requisition - No FI entry it is just an order no Financial impact in the transaction.
- Purchase Order Creation - No FI entry it is just an order no Financial impact in the transaction.
- Good Receipt – FI Entry is created in this step , the following entry is posted.
Stock A/c Dr
To GR/IR A/c Cr
- Quality Check - No FI entry it is just an order no Financial impact in the transaction. Note: If the QC fails the Goods are returned and the Goods return Process is triggered. If QC is successful the invoice is made.
- Invoice Verification: FI entry is created and the following FI entry is posted.
GR/IR AC Dr
To Vendor A/C Cr
The Taxes, expense price difference, and so on, are also posted.
- Invoice is released for Payment: Once the invoice is posted the invoice can be checked by a higher authority and released for making payments to the vendor. No FI entry is passed.
- Payments: The Invoice to be paid is selected from the Vendor Master Data and payment against the same is made. The following Accounting entry is triggered:
Vendor A/C Dr.
To Bank A/c Cr.
- Open Items are cleared in the Vendor Master:
Vendor Master
Debit Credit
Pt. 8. Bank Account A/c xxx Pt. 6. GR/IR Account xxx
Total xxx Total xxx
Now when we talk about integration we usually mean the way in which FI entries are triggered by MM module. In the above process certain entries flow automatically in FI when the entry is posted in the MM Module. How are these automatic entries triggered? To post entries we need to pick up certain GL Accounts according to what business transaction is being carried out. This is called Account determination in SAP. All FI inter Module Account determination is done by configuration in the Standard Transaction codes provided by SAP. Once we map our required GL Accounts the system automatically picks the accounts and posts the FI entry.
The Following configuration steps help us determine Accounts for the automatic FI entries.
Valuation Area:
Stock of a Material owned by a Company. Valuation area defines the organization level at which materials are Valuated. SAP provides two options for doing the same:
- Valuation at Plant Level-
All Materials are valuated at Plant Level.
- Valuation at Company Code Level:
All Materials in all the Plants of a Company are valuated at Company Code level.
Valuated Stock:
Total Valuatedstock = Stock in unrestricted use + Stock in Transit + Stock in QA.
Material Type:
This defines the type of Material. For example, Raw Material , Finished Goods, Semi-finished goods, and so on.
Movement Type:
This defines the type of material movement from one place to another. The movement type enables the system to find predefined posting rules determining how the stock and consumption accounts are to be posted. All the possible goods movement are already defined by Standard SAP. EG 101 refers to Goods Receipt.
Valuation Class:
Valuation Class is defined in Material Master record in the combination of Plant. Valuation Class allows posting of Stock Values of:
- Materials of the same material type to different GL Account (Different Valuation Class is assigned in different plants for the same material)
- Materials of different material type to same GL Account (Same Valuation Class is assigned to materials of different material type)
Valuation grouping code:
Valuation grouping code combines the Valuation areas having the same business properties for the Account Determination. This reduces the number of entries to be created for automatic account determination for the stock postings. For example, Valuation Area 1 and 2 are required to be posted to the same GL Account. These are grouped to the Valuation Code ABC and the GL Account is determined on Valuation Grouping Code and Valuation Class.
Account Modification /General Modification:
This key is used to determine a different GL Account for the same kind of goods movement based on an origin and a target.
For example, during goods issue, Offsetting Account (GR/IR Account) is determined from the transaction key GBB. Now if the business wants to post to different GL Account of goods issue to cost center or to Internal orders for same material and plant combination, Account modifiers can help. Below are the standard account modifiers provided by SAP for the Offsetting Account determination Key GBB.
- AUF- for goods receipts for production orders with Account Assignment.
- BSA-for initial entries of stock balances.
- INV-for expenses/revenue from inventory differences
And so on. The same can be checked in the system and configured as per the user requirement and business postings. As the Above derivation of accounts is a stepwise procedure. SAP also provides with a tool called Account determination simulator, which works faster to show the Account determination on SAP screen.
Some examples of other Business processes, which triggers FI MM Integration, would be as below:
- Plant to Plant Transfers
- Subcontracting Process
- Job work Process