In SAP ERP there are various sub ledgers i.e. Account Receivable, Accounts Payables, like wise let us study Asset Accounting, its organizational hierarchy and its Master Data. Financial Accounting consists of an organizational hierarchy and it is integrated to the Asset Account Organizational Hierarchy. This leads to intra module integration and inter module integration. AssetAccounting is also integrated with Controlling Module Material Management Module. Let us see this link between FI, CO, MM and Asset Accounting.
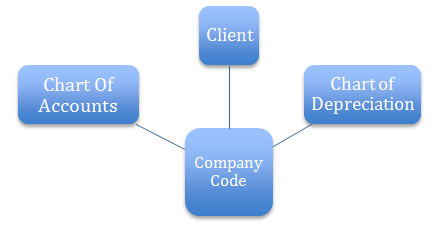
Chart Of Accounts
The chart of accounts is a variant, which contains the structure and the basic information about general ledger accounts. All the GL Accounts are comprised in the chart of accounts. It is the basic structure consisting of the entire general ledger Accounts.
Client
The Client is the highest level in the SAP system hierarchy. It also denotes the specific logical system you are working on. Specifications that you make on the client level are applied to all the company codes under that client.
Company Code
Each Company Code is an independent accounting unit. The legally required balance sheet and profit and loss statement are created on the company code level. A company code represents an independent balancing/legal accounting entity.
Business Area
Business areas represent separate areas of operation within an organization and can be used across company codes. They are balancing entities that can create their own set of financial statements for internal purposes. It is therefore possible to save and evaluate transaction figures for each business area.
Profit Center
The profit center evaluates the success of individual independent areas within a company. These areas are responsible for costs and revenue. The aim of profit center invoice is to provide an internal analysis of profits. From an accounting point of view it must be determined whether only a profit and loss statement at profit center level is to be created or whether a financial statement is also to be created.(If a Balance sheet is required, like the business area the Document splitting functionality needs to be activated on Profit center level.)
Plant
As a part of the Logistics organizational structure, Plants are defined in SAP. The Plant is an operating area or a branch or a location within a company. Each plant is assigned to a single company code it is a physical location where activates take place in a company. One company Code can have multiple Plants.
Cost center
Organizational unit, within a Controlling Module, that represents a clearly defined location where costs occur. You can make organizational divisions on the basis of functional settlement related, activity-related or responsibility related.
Chart of Depreciation
Chart of depreciation in SAP comprises of all the necessary depreciation areas in Asset Accounting. These contain predefined depreciation Areas. Chart Of depreciation is a client level and can be used by Multiple Company codes simultaneously.
Depreciation Area
Depreciation area in a chart of depreciation is defined with a two digit numeric key. The depreciation Area reflects the accounting principles in Chart of depreciation. The various depreciation areas available in system are as below
- 01 Book Depreciation
- 02 Special tax depreciation
- 20 Cost Accounting Depreciation
- 30 Consolidated Balance sheet (Local Currency)
- 31 Consolidated Balance Sheet (Group Currency)
- 32 Book Depreciation in Group Currency
And so on.
01 Depreciation Area is considered as the Leading depreciation Area. It always reflects the Local Accounting Principle of calculating depreciation in SAP.
Now with the above configuration is SAP Asset Accounting is ready to use.
- Firstly a company code is set up in Financial Accounting.
- A Chart Of Accounts (Variant at Client level) is Assigned to the Company Code
- A Chart of Depreciation (Variant at Client Level) is assigned to the Company code
Asset Master records created In SAP.
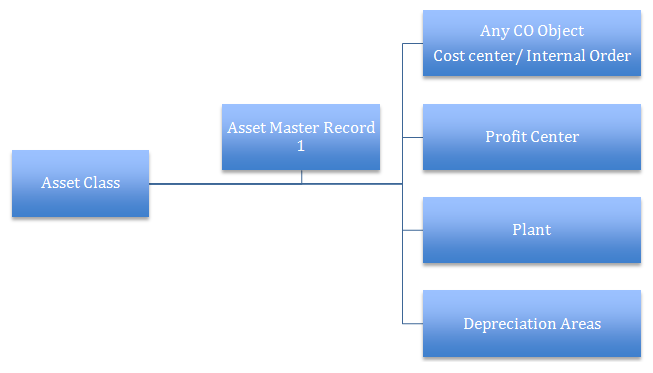
Asset Class
Asset Masters are assigned or grouped to Asset Classes. Asset Class like Chart of Accounts and Chart of Depreciation is also at Client level but is individual and not assigned to a company ode in configuration. Asset Class consist of a master data section and a depreciation area section.
An asset is created in a company code under the Asset Classhence all the depreciation Areas are attached to the Asset Master Record through the chart of depreciation assigned to the Company code in which the Asset is created.
Thus the Asset is created in a particular Company Code and under a particular Asset Class.
Asset Class is the main criterion for classifying assets.
Examples of Asset Classes would be:
- Furniture and Fixtures
- Land
- Buildings
And so on.
Below represent the integration of Asset Accounting Various other Modules Controlling, Material Management etc. The Asset Master record is attached to a relevant CO object a cost center internal order WBS element etc. It is also attached to a Plant a physical location where the Asset is used and integrating with MM module.
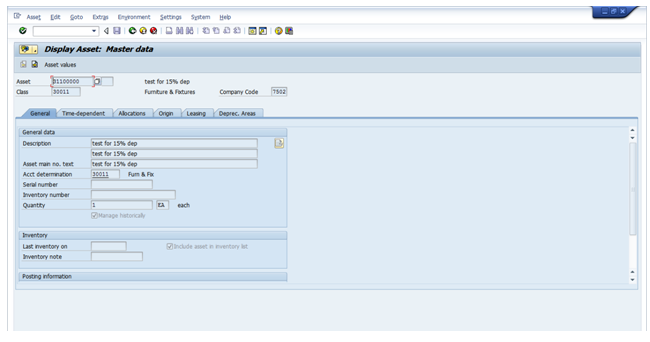
Below is the SAP screen for Asset Master Creation, all the tabs are shown one after another with all the necessary screens to be maintained for a master record.
General Data Tab:
- Description of the asset
- Number of assets
- Account determination – GL accounts for the Asset Postings
- Capitalization date
- Date for Ordinary Depreciation calculation
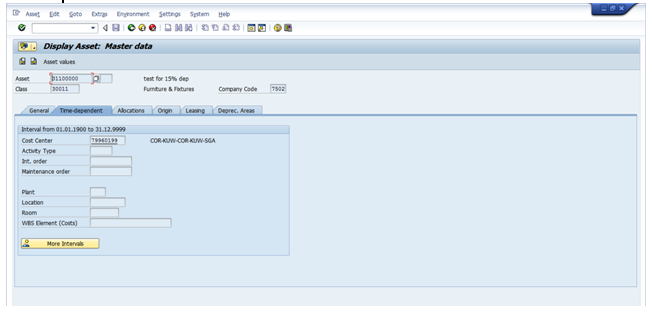
Time dependent tab:
The assignments made in this tab can be maintained for validity periods i.e from and to period.
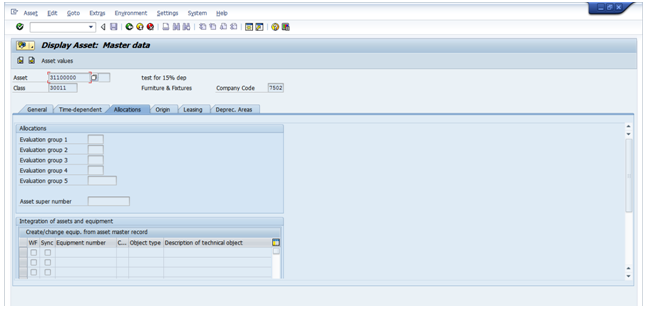
Allocation Tab:
- This tab allows freely definable evaluation groups for assets
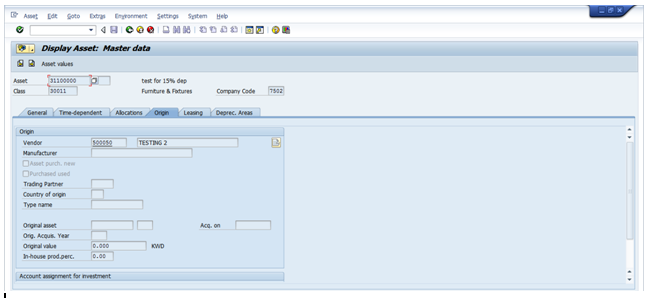
Origin Tab:
- Vendor from which the asset is purchased
- If manufactured entry is made in these fields
- In legacy data if the asset has a legacy asset number can be maintained here (Original Asset, acquisition year)
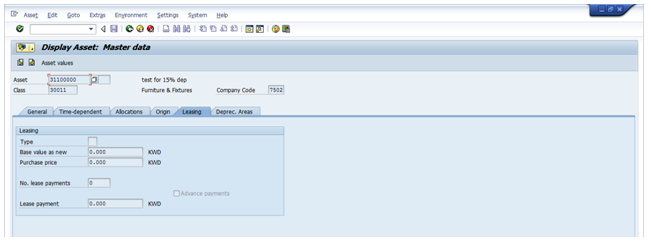
Leasing Tab:
- Lease related information maintained
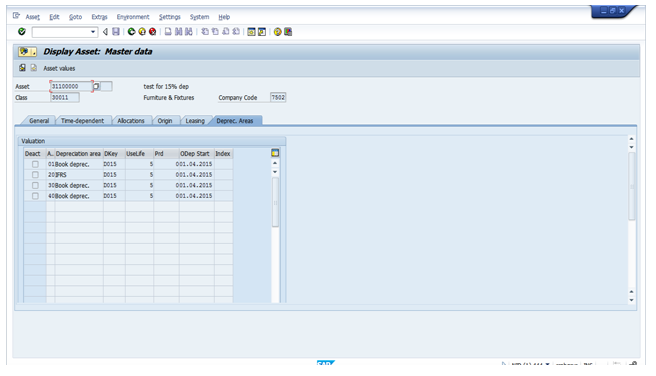
Depreciation Tab:
- The active/deactivated depreciation Areas.
- Depreciation keys
- Useful Life
Ordinary dep calculation starts date.
- Lease related information maintained
Some Important Points to be taken in consideration as per system perspective.
1. Each Company Code uses one (operative Chart of Accounts) and one chart of Depreciation.
2. All or several Company Codes can work with the same chart of Accounts and the same chart of depreciation.
3. Different Valuation Approaches are mapped in SAP system by means of depreciation area.
4. User can define its own depreciation areas for different valuation purposes.
5. An Asset Class can be linked to multiple Charts of Depreciation. This enables a globally uniform class catalog in spite of different depreciation areas.