This tutorial is a continuation of Oracle Fusion Payroll - Fusion Overview(Part 1)
Oracle Fusion Overview - Common Terminologies in Fusion Applications
● User Interface (UI) Regions ✓
● Navigator ✓
● Search ✓
● Notification and Approvals ✓
● Help ✓
● Data Management ✓
● Process, Reports and Analytics ✓
● Personalisation
● Troubleshooting
● Accessibility
Personalisation
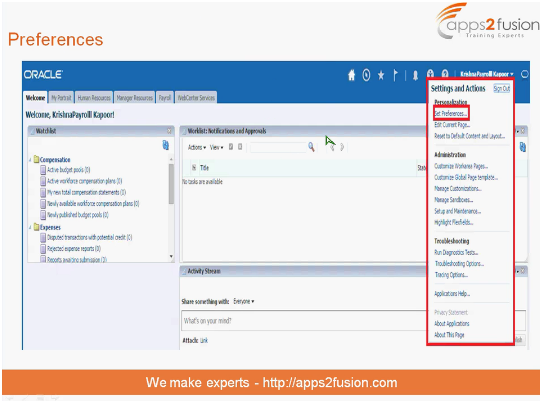
Fig. 1 - Navigating to the Preferences menu
To set and edit preferences, click on the Set Preferences option from the drop-down under your login.
The preferences menu. Edit your Watchlist, Access
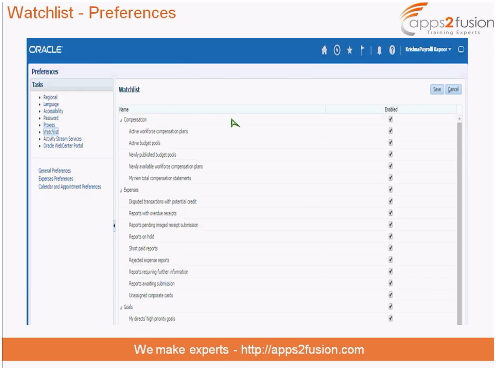
Fig. 3 - Watchlist Preferences screen
Other than tweaking your preferences (like language, timezone, watchlists, etc.) according to your specific requirements, Fusion Applications provide a variety of personalisation options (to access, go to Settings & Actions -> Administration and choose the relevant option):
● Customising the pages in the Sandboxes through Oracle Composer.
● Customising Security and Flexfields
You can first test your customised settings before publishing it.
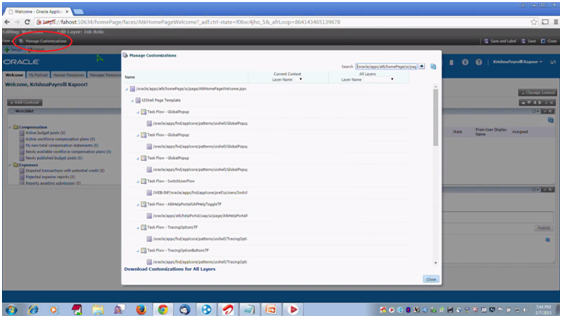
Fig. 4 - Managing customisations for pages
Troubleshooting
Fig. 5 - The Troubleshooting screen
The Troubleshooting menu can be accessed through Settings & Actions -> Troubleshooting.
It can be used to perform diagnostic tests with logging and traces, which are executed through the Oracle Applications Diagnostics Work Area. These are product-specific, and are provided before starting transactions.
Accessibility
The Accessibility screen provides options for setting the accessibility mode, colour contrast, and font size.
Other Concepts of Fusion Applications
Some other concepts relating to Fusion Applications are discussed below:
● Dashboards and Work Areas
● Security
● Seed Data
● Flexfields
● Lookups
● Value Sets
● Date Effectivity
● Trees
Dashboards and Work Areas
Dashboards:
Dashboards contain an aggregation of information relevant to a particular role or domain. They act as launch points for the Oracle Fusion Applications.
Dashboards are operational. They provide an overview to support users’ day-to-day activities. They can also be used to make a strategic decision, as they provide trends and aggregation of information to support users’ longer-term activities (e.g. in the Payroll Dashboard, you can view the number of processes and the phases they are in).
Dashboards are also transaction-based and BI-based, meaning they can be integrated with Business Intelligence. They can come in Home dashboards or Standalone dashboards on the UI.
Work Areas:
Work Areas are a complete set of tasks, searches, reports, embedded analytics, and other content that a user needs to accomplish a business goal. The work areas are scoped depending on a set of user roles and tasks related to a business goal. The key criteria of work areas is that users should not have to navigate among multiple work areas to accomplish a particular goal.
Security
Fusion Applications are fully secure. Unless you have a role assigned to you, you cannot perform any task. As it is role-based security, it controls who (the assigned role) can do what (the function to be performed) on which data.
The following are the different types of roles along with a Payroll example:
● Data roles - They combine a worker’s job with the data to be accessed.
○ The HCM data role Payroll Administrator Payroll US combines the Payroll Administrator job with the Payroll US data scope.
● Abstract roles - They represent a worker’s role in the enterprise independent of his job.
○ Employee, Contingent Worker, and Line Manager are predefined abstract roles in Oracle Fusion HCM.
● Job roles - They represent the job that you hire a worker to perform
○ Human Resource Analyst and Payroll Manager.
● Duty roles - They represent the individual duties that the workers perform as part of their job. The job and abstract roles inherit duty roles.
○ Granting access to work areas, dashboards, task flows, application pages, reports, batch programs, etc.
Roles are customisable, as depicted in the above illustration. The different roles of the user is shown below the user’s name.
Seed Data
They are the data shipped by Oracle. This can be done through lookups, messages, product-specific data, country-specific data, etc.
HCM provides a lot of data in the entire Fusion Application - more than 50%. Within HCM, Payroll and Localisations account for 60-70% of the data.
Flexfields
Flexfields are customisable UI components that have built-in flexibility, so that users can define reporting structures that are relevant to their specific organisations.
There are three types of flexfields:
● Key flexfields (KFF): (Mandatory) They are configurable multi-part intelligent keys used to implement Item Number, Account Number, etc.
● Descriptive Flexfields (DFF): (Optional) They have the ability to extend the data model with additional attributes.
● Extensive Flexfields (EFF): They are similar to DFF, with some additional features: the number of configurable segments is not fixed, and they support one-to-many relationships between the entity and extended attribute rows.
Date Effectivity
Date Effectivity is a concept that is extensively used in HCM. It is a mechanism to have multiple versions of instances of an entity, depending on specific dates. HCM also has Multiple Changes per Day (MCD). The lifespan for a date-effective entity is from 01 Jan 1951 to 31 Dec 4712.
The operations that are available are: Correct (change the entity data for the entire lifespan), Update (create an extra version of the entity on a particular date), Delete this Change (delete a specific version of the entity), Delete (delete the entire entity).
Trees
Trees are a graphical representation of hierarchical data, such as the structure of your organisation. This organises data in applications into a hierarchical fashion, and allows you to create tree hierarchies based on specific data.The tree structure is a way of describing a hierarchy, and is an instance of this hierarchy. In HCM, trees are extensively used. There are different types of trees like Department Trees, Organisation Trees, Position Trees, etc.